

Location: Ground Floor
Includes biochemistry, hematology, immunology, pathology, molecular biology, cytology, blood bank, specific testing & diagnosis of infectious diseases. Biochemical tests & all other tests are carried out in this section & neonatal bilirubin tests & Cardiac markers are done emergently in less than one hour. Nikan Hospital Blood Bank Laboratories provide the best Service in transfusion of blood & blood products in the shortest time Launching molecule section at Nikan Hospital Laboratory is one of our most outstanding successes that daily reports PCR Tests & Speeds up the process of
patient's treatment.

Ultrasound (also called sonography or ultrasonography) is a noninvasive imaging test. An ultrasound picture is called a sonogram. Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to create real-time pictures or video of internal organs or other soft tissues, such as blood vessels.
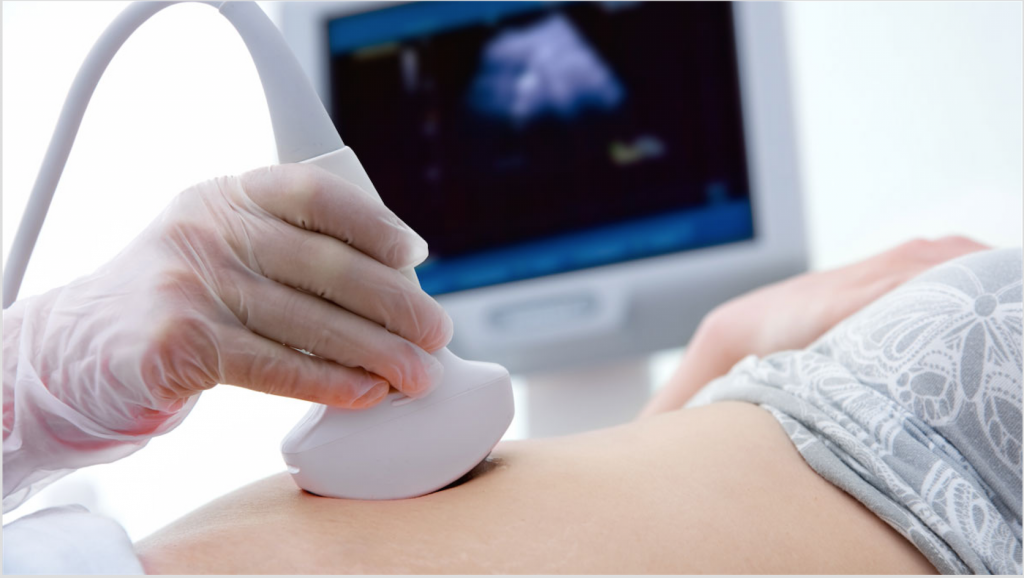
How does an ultrasound work?
During an ultrasound, a healthcare provider passes a device called a transducer or probe over an area of your body or inside a body opening. The provider applies a thin layer of gel to your skin so that the ultrasound waves are transmitted from the transducer through the gel and into your body.
The probe converts electrical current into high-frequency sound waves and sends the waves into your body’s tissue. You can’t hear the sound waves.
Sound waves bounce off structures inside your body and back to the probe, which converts the waves into electrical signals. A computer then converts the pattern of electrical signals into real-time images or videos, which are displayed on a computer screen nearby.
Location: Ground Floor
Radiology is one of the diagnostic methods.
The imaging department of Salahedin Ayuobi Hospital possesses the most modern equipment and machines and performs all kinds of common and routine imaging processes for its respectable patients round- the- clock.
This center is equipped with PACS which makes it possible for doctors all around the world to access the images through the internet.
What is mammography?
Mammography is an x-ray imaging method used to examine the breast for the early detection of cancer and other breast diseases. It is used as both a diagnostic and screening tool.
How does it work?
During a mammogram, a patient’s breast is placed on a flat support plate and compressed with a parallel plate called a paddle. An x-ray machine produces a small burst of x-rays that pass through the breast to a detector located on the opposite side. The detector can be either a photographic film plate, which captures the x-ray image on film, or a solid-state detector, which transmits electronic signals to a computer to form a digital image. The images produced are called mammograms.
On a film mammogram, low density tissues, such as fat, appear translucent (i.e. darker shades of gray approaching the black background) whereas areas of dense tissue, such as connective and glandular tissue or tumors, appear whiter on a gray background. In a standard mammogram, both a top and a side view are taken of each breast, although extra views may be taken if the physician is concerned about a suspicious area of the breast..jpeg)
Location: Emergency unit
An electrocardiogram is a painless, noninvasive way to help diagnose many common heart problems. A health care provider might use an electrocardiogram to determine or detect: Irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias) If blocked or narrowed arteries in the heart (coronary artery disease) are causing chest pain or a heart attack Whether you have had a previous heart attack. How well certain heart disease treatments, such as a pacemaker, are working.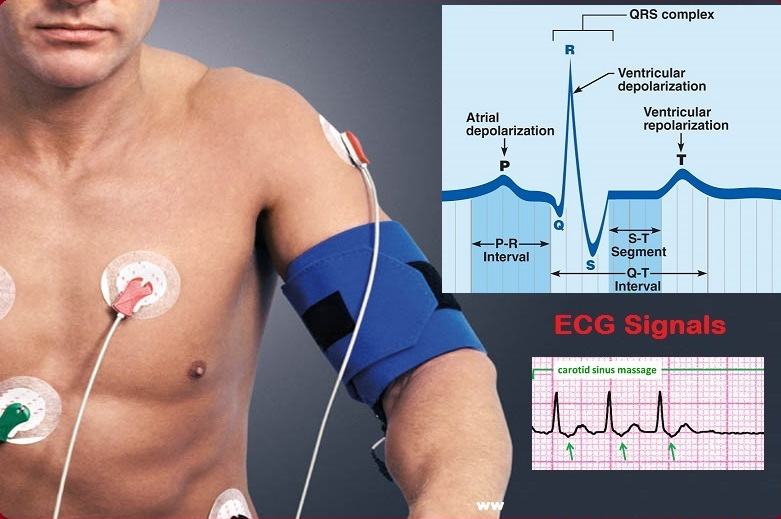
Echocardiography, also known as cardiac ultrasound, is the use of ultrasound to examine the heart. It is a type of medical imaging, using standard ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound. The visual image formed using this technique is called an echocardiogram, a cardiac echo, or simply an echo.